Every click today carries trust. Whether you shop on a global e-commerce site, chat on a messaging app, or log in to the cloud, you rely on your data staying unread and unaltered. This is where encryption comes in. It is not a technical ornament; it is the shield that safeguards the relationship between people, businesses, and technology on the internet.
Encryption creates a safe pathway for data. It is why payments, private chats, and file transfers remain trustworthy, even when people and companies are far apart.
Trust grows when encryption is well-designed: strong key management, clear policies, and a user-friendly experience. Weak implementation leads to risks, data leaks, and loss of credibility.
The Core of Trust: What Encryption Is
At its simplest, encryption turns readable messages into text that cannot be understood without the right key. There are two main types. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of public and private keys, enabling secure exchanges even between strangers. When paired with the right protocols, it creates a private channel over the public internet.
Its value is practical. If someone intercepts Wi-Fi traffic, encryption renders it useless. If a backup drive is stolen, it is just empty data without the decryption key. Trust is not a guess. It is built on sound cryptography and good practices.
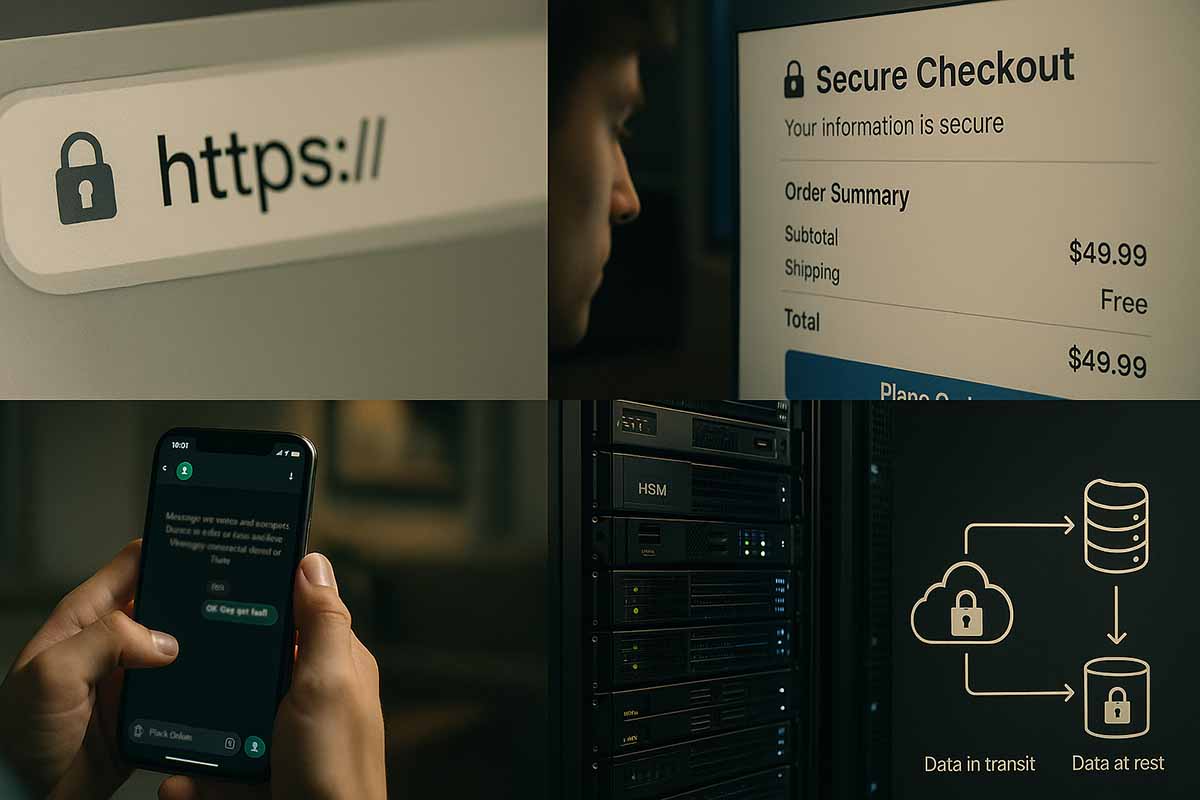
HTTPS, TLS, and Certificates: How Web Trust Begins
When you see a padlock in the browser’s address bar, HTTPS is running. HTTPS relies on TLS, which establishes an encrypted session between the browser and the server. Behind this are public key cryptography and certificate authorities that verify a website’s identity.
Extra safeguards, such as certificate transparency and strict issuance policies, create a clearer chain of trust. Careful implementation reduces the chance of fake identities. Neglect leads to weaknesses, such as outdated cipher suites or misconfigurations that invite attacks.
Human Habits: Private Chats and Secure Checkout
Families share photos and voice messages that should remain unseen by outsiders. Many apps use end-to-end encryption, meaning only the sender’s and receiver’s devices have the keys. Even the provider cannot read the content.
When shopping online, secure transport layers and proper tokenization matter. Raw card data should never circulate. When customers see clear security indicators and smooth page flow, their confidence rises. This leads to fewer abandoned carts and more repeat purchases.
Organizations: Trust as an Advantage
Every company is a data custodian. Strong encryption reduces overall risk and incident costs. It also makes compliance with regional standards easier. Boards and regulators want proof not just of a security plan but of active implementation.
A clear protection story boosts reputation, opening doors to new markets and partnerships. Failures, on the other hand, can erode trust quickly, and regaining it is difficult.
Data in Transit and Data at Rest
Protection has two stages. First is data in transit, secured by TLS for the web, mTLS for server-to-server connections, and encryption for queues and brokers. Second is data at rest, covering databases, object storage, and backups. This stage typically includes strict access controls and separate key management.
Both are essential. Many breaches stem from unencrypted snapshots, log files, or outdated backups. Others occur due to misconfigured network channels. Discipline on both ends forms a complete defense.
The Heart of the System: Key Management
Even the strongest algorithm fails with poor key handling. Key management defines who can create, use, and delete keys, and requires regular rotation and audit trails. Many companies use cloud KMS or HSM for hardware-backed protection.
Separation of duties is vital. No single person should control both key creation and use. There must be processes for emergencies such as lost or compromised keys. With a solid foundation, operations stay smooth and costs stay manageable.
Machine-to-Machine Trust and APIs
Most traffic today comes from services talking to other services. APIs need strong identity checks. mTLS supports mutual authentication, while signed tokens verify request authenticity.
Consistency helps. A central place for managing certificates, automated renewals, clear cipher policies, and allowed protocol versions reduces human error.
Privacy, Regulation, and Global Standards
Laws differ across regions but share one goal: protecting people. Encryption is a key tool. Processing purposes must be clear, and sensitive records should remain encrypted throughout their lifecycle. This includes redaction, retention, and proper deletion once no longer needed.
Building privacy into the design early makes market entry easier and discussions with auditors and partners smoother. It shows commitment backed by a functioning system.
Industry and IoT: Device Identity
In factories, hospitals, and transportation, thousands of devices connect to networks. Each needs its own identity and trustworthy certificate. Firmware signing prevents harmful updates. Without proper authentication and encryption, fake devices can slip through.
Costs do not need to skyrocket immediately. Start with risk-based certificate deployment and secure onboarding. As fleets grow, automated key rotation and clear device lifecycles become essential.
Common Obstacles and Quick Fixes
Some frequent issues and practical steps include:
- Slow systems due to encryption settings: check hardware acceleration and use modern cipher suites.
- Poor user experience: display clear security signals and avoid excessive prompts.
- Weak key management: use cloud KMS or HSM with rotation and auditing.
- Gaps in visibility: use centralized logging for TLS handshakes, certificates, and key access.
Measuring Trust: Knowing It Works
Checklists are not enough. You need metrics. Track the percentage of internal and external traffic using the latest TLS version. Measure how quickly certificates are renewed before expiry. Monitor unauthorized access attempts to key vaults.
Customer signals also matter. Lower abandoned checkout rates and higher opt-in to account security suggest your protections are noticed and appreciated.
User Experience: Security Without Friction
Trust grows when security feels effortless. Two things help: visible indicators such as padlocks, proper domains, and consistent payment flows, and modern authentication methods like passkeys and hardware keys, which verify identity and block phishing.
Avoid long processes. Use risk signals to reduce extra steps when risk is low. Upgrade defaults, but explain clearly when user action is needed.
Business Alignment: From Cost to Value
Some leaders see encryption as an expense. In reality, fewer incidents mean fewer disruptions. Faster entry into regions with strict standards means new revenue. A clear security story supports sales with demanding procurement processes.
Reputation also grows. When partners trust you, integrations move faster. When the public sees genuine care for privacy, brand loyalty increases. These benefits may be hard to measure daily but are felt over time.
Research Shifts: Post-Quantum and Beyond
Changes are coming to cryptography. Current algorithms may weaken against future computing advances. This is why universities and research bodies are exploring alternatives. A hybrid approach may work during transitions. The smart move now is a crypto inventory. Identify current protocols and libraries, and prepare for migration when new standards are ready.
Other methods are gaining ground, such as enabling collaboration without exposing underlying data. In some cases, aggregated information can be analyzed while personal details remain private. Careful design is essential, but the balance between utility and privacy is promising.
Practical Guide for Teams
Start with discovery. Map all data flows from clients to databases and back, marking sensitive points. Once clear, it is easier to choose protocols and key policies.
Use the latest stable TLS for all traffic, avoiding outdated cipher suites. Set a minimum version and enforce it on load balancers and service meshes.
Create a central key management policy, granting access only to those who need it. Implement rotation and detailed logging. Separate production and testing environments.
Support developers with approved libraries, sample code, and safe configuration rules. The easier the secure path, the more likely it is to be followed.
Manage certificates with automated renewal, early alerts, and domain control checks. This prevents sudden outages from expired certificates.
Prepare an incident playbook. If a breach is suspected, have ready steps for key rotation, token revocation, and increased monitoring. A rehearsed plan ensures calm, clear responses to customers.
A Short Story: A Global Brand and the Strength of Privacy
Consider a streaming service with audiences across continents. Users once complained about account takeovers. The team improved HTTPS settings, added modern authentication, and automated certificate renewal. They also simplified their privacy and security policy page. Gradually, account takeover reports dropped, and trust grew without flashy announcements. Quiet work, but customers felt the difference.
Why Clear Communication Matters
Technology is the foundation, but people create trust. Explaining why a padlock appears, why an extra login step is needed, and how data is protected helps users understand benefits. This makes cooperation and loyalty more likely.
Not every page needs technical language. Short, honest, and consistent explanations work best. Announce changes, and in case of incidents, communicate with care and clarity. This shows respect at the heart of your design.
Trust as a Long-Term Commitment
Threats evolve. Data and connections keep growing. One lesson remains: strong encryption and careful key management form a quiet yet strong wall around people and businesses, allowing the world to operate with confidence.
Online trust does not happen by accident. It is built into every line of code, every policy, and every message to users. Choosing the right design today means a safer tomorrow for all.


No Comments